
The selection of the right packaging materials is crucial to ensuring the protection and safe delivery of products. There are two main types of packaging materials available on the market: cardboard and corrugated boxes.
Although they look very similar, in reality, these two materials are completely different in characteristics that influence their durability, strength, and how they are used. Today we’ll discuss the durability and strength testing insights of cardboard and corrugated boxes. We’ll also dive deep into the analysis of their benefits and limitations.
Cardboard is one of the most popular packaging materials. It’s known for its versatility and ease of use. According to reports, cardboard is used as packaging material in approximately 90% of goods transported. It is made up of a thick layer of paper waste or fresh wood pulp structure that allows it to be used in various ways. This material is typically used in the production of lightweight packaging, such as retail boxes, product packaging, and small shipping containers. There are different forms of cardboard, including chipboard used in cereal boxes, and solid bleached sulfate (SBS), which is often used in premium product packaging.
Corrugated boxes are a bit more complex as compared to cardboard. They have a wavy structure sandwiched between two or more layers of paper. Also, this sandwich design of corrugated boxes can tolerate more stress and distribute the energy evenly throughout the box, which keeps the product inside the box safe. You’ll find these boxes in different forms, such as single-wall, double-wall, and triple-wall, each offering varying degrees of protection and load capacity.
Cardboard and corrugated boxes are two completely different materials, although they seem to be similar. People often mistake corrugated boxes for cardboard. Check out How to Choose Between Cardboard and Corrugated Boxes for Your Business?
Cardboard is a single sheet of heavy-duty paper or paperboard, and it’s thinner and lighter as compared to corrugated boxes. On the other hand, corrugated boxes consist of multiple layers of heavy-duty paper or paper boards. They have at least three layers, in which the middle layer forms a wavy structure that makes it more durable as compared to cardboard.

With the structural comparison of both cardboard and corrugated boxes, we can clearly say that corrugated boxes are more durable and reliable than cardboard. You can perform multiple tests to check the durability and strength of cardboard and corrugated boxes.
A product waffles a lot during transportation, so the packaging material must withstand vibrations during transportation, handling, and distribution. This test mimics the environment and tests the strength of the packaging material.
While transporting a product, it passes through a lot of environmental conditions, and a good packaging material must be resistant to these conditions. This test aims to analyse the absorbency of the packaging material to check if the material is resistant to moisture or not.
This test is performed to check the strength of a corrugated box. It aims to check if the corrugated box is able to handle sudden shock or impact or not.
The pull test aims to check the strength and durability of cardboard and corrugated boxes by applying force to see if they can resist stress during transportation and handling.
As the name suggests, the test aims to check if the packaging material can withstand any sudden impact through a sharp object.
Sometimes products get damaged during loading and unloading. The Forklift Simulation Test aims to check if the packaging material can protect the product from deformation during these processes.
During this test, boxes are exposed to various environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures and humidity, to assess their durability.
The compression test, as the name suggests, aims to check the maximum load a box can bear before collapsing by simulating the stacking pressure it would experience during storage and transportation.
This test is the same as the compression test but for an edge. Through this test, we can assess the vertical compression strength of the box’s edges. It helps evaluate the box’s stacking capability.
During the drop test, a packing box is dropped from various angles to check the strength and durability of cardboard and corrugated boxes. It ensures that the product is safe during transportation and handling, even if it drops.
A tear-resistant test aims to check how much stretch force a box can resist before it gets torn.
It tests how well-printed graphics and labels stick to the box, ensuring they remain securely attached and do not rub off or smudge during handling and transportation.
A good packaging material should also protect the product from environmental conditions like moisture, temperature, sunlight, and other factors. Although both the packaging materials, cardboard and corrugated boxes, have similar materials, their structural differences make them completely different from each other.
Cardboard, due to its single-layer design, is particularly vulnerable to moisture and heat, which can compromise its structural integrity. While corrugated boxes are also affected by environmental conditions, their multi-layered design offers better resistance to such factors, ensuring more reliable performance in challenging environments.
Cardboard is a lightweight (often) shiny and cost-effective packaging material. Due to this, it can be used as packaging material for small products like cereals, small toys, board games, gadgets, etc. Its simplicity and ease of customization make it a preferred choice for retail packaging.
Unlike cardboard, corrugated boxes are used in packing medium-to-large products because of their strength and durability. It comes in multiple strength options that depend on the number of layers they have. However, corrugated boxes are more expensive because they have multiple layers and are comparatively heavier than cardboard.
Read more: Cardboard Vs. Corrugated Boxes: Understanding the Differences and Uses
The main difference between cardboard and corrugated boxes is the structural design of both materials. Cardboard is a single-layer paper sheet, whereas corrugated boxes consist of multiple layers, which makes it more reliable for product safety during delivery.
Cardboard is clearly a more cost-effective packaging material, but it should be decided by the packaging requirements of the product. If you have a sensitive product or a medium-to-large product, then you must go for corrugated boxes, as they offer more strength and durability.
Certainly, corrugated cardboard is stronger than cardboard, as they have multiple layers and can handle a lot of pressure.
The Bursting Strength Test, or the mullen test, can be performed as a strength test for corrugated boxes. This test shows how tough the walls of corrugated boxes are and how much pressure they can handle.
Cardboard is ideal for packaging small retail products like cereals, toys, etc., whereas corrugated boxes can be used for medium-to-large products and also for sensitive products that require more packaging strength.
Tags :
Share the article:
Recent Posts

Today packaging isn’t just about the containment and protection of the product
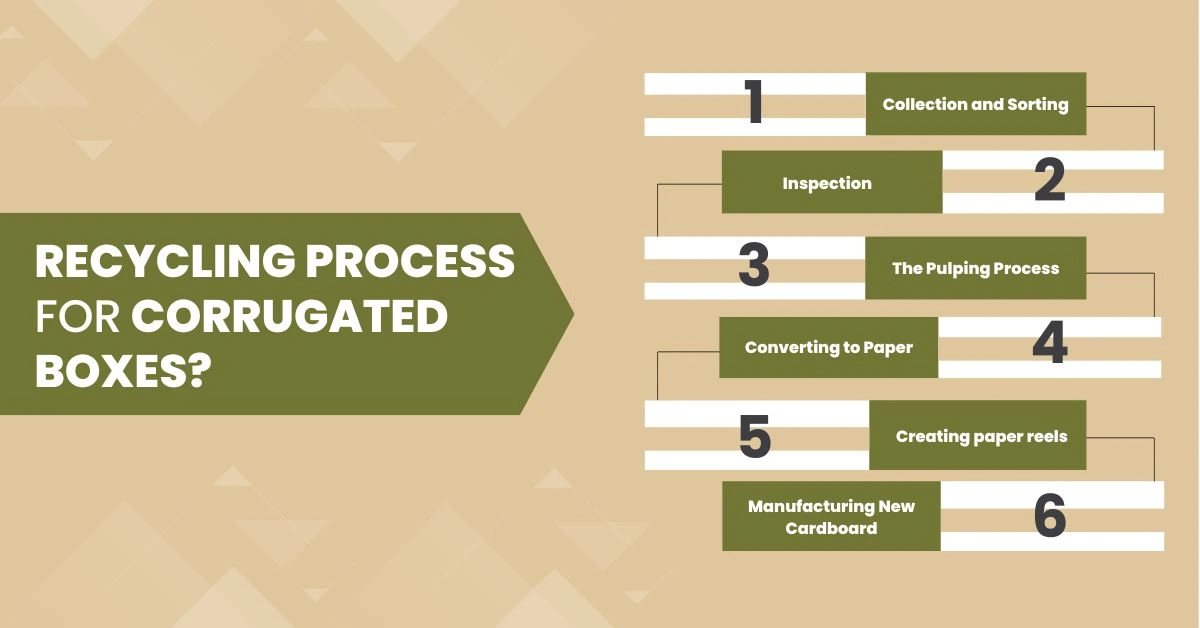
We use corrugated boxes on a regular basis to store our products

The selection of the right packaging materials is crucial to ensuring the

Corrugated cartons are lightweight structures that are commonly used to pack various

Corrugated boxes are containers that we commonly use to store and ship
Packaging is one of the most important parts of any business, and

Whenever we purchase any items or products either online or offline, they

In the world of shipping and packaging, two players that stand out
Contact Us
Customer Support
Company Information
Copyright © 2025 Pacfo International Private Limited